There are several types of hypoxia, such as perinatal hypoxia, hypoxic or anoxic hypoxia, haemic or anaemic hypoxia, ischaemic hypoxia, histotoxic or cytotoxic hypoxia, and hypoxaemic hypoxia.
Perinatal hypoxia
Affects neonates, especially due to complications during childbirth that interfere with oxygen supply, potentially resulting in long-term brain damage.
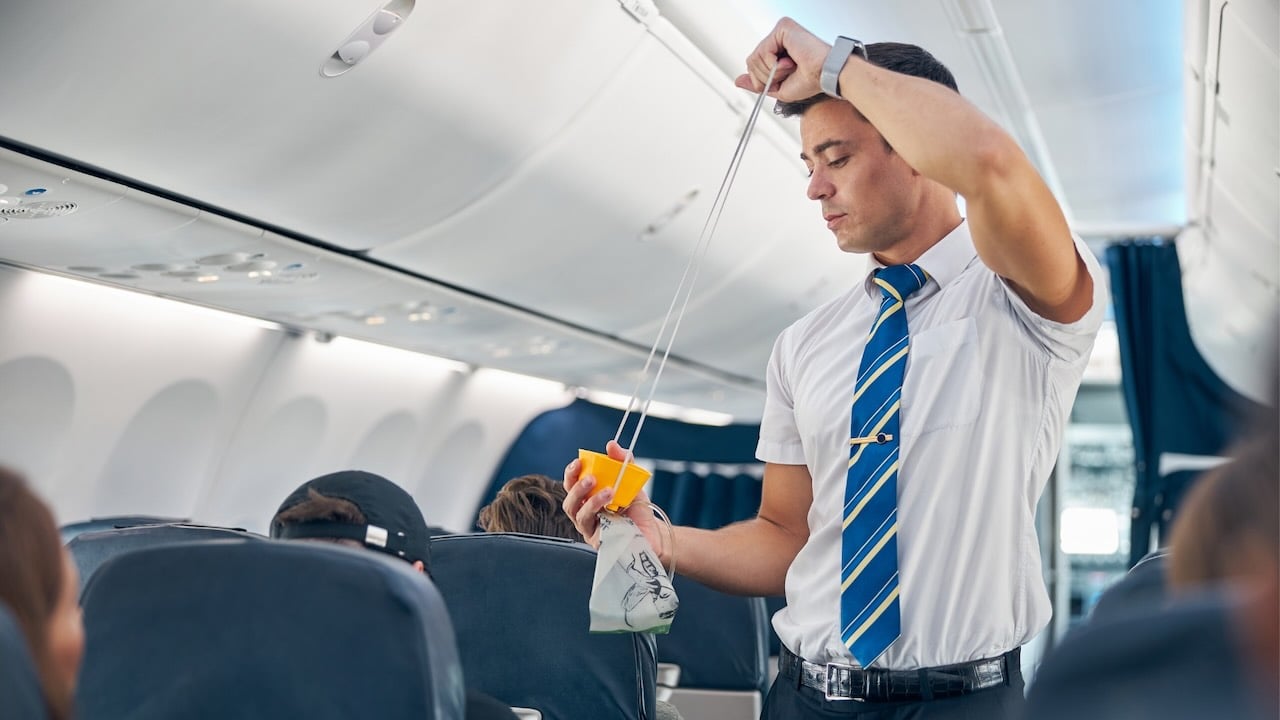
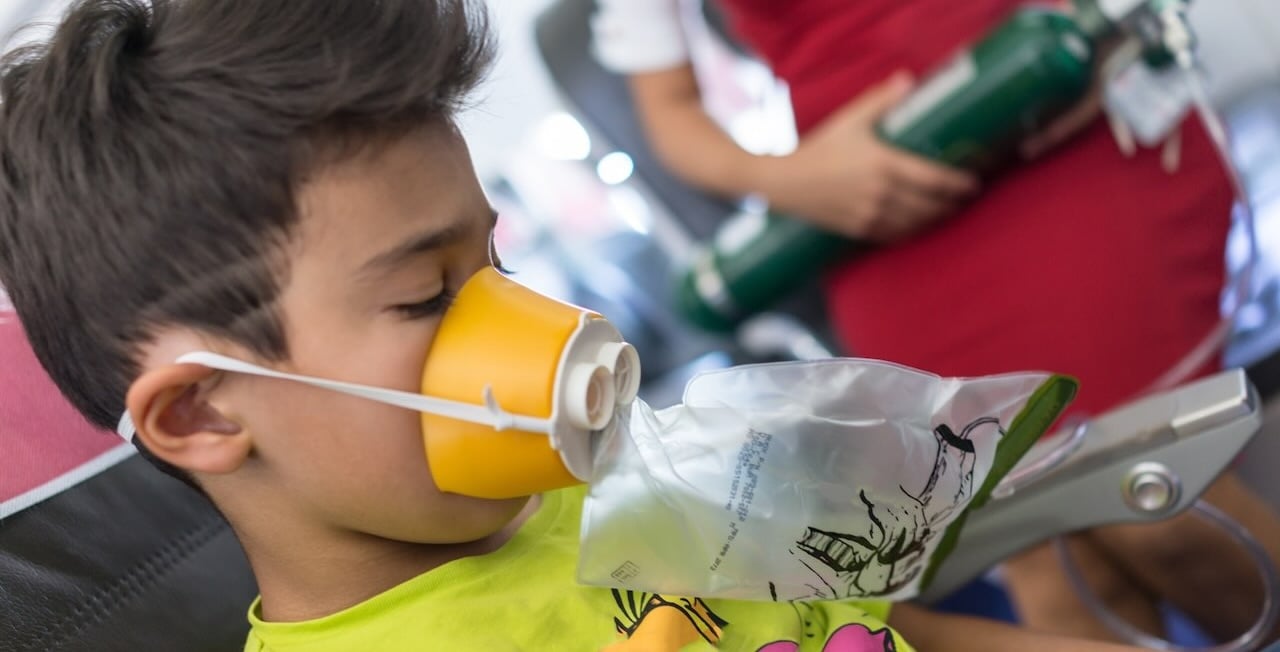
Hypoxic hypoxia
This is the most common in aviation, caused by insufficient partial oxygen pressure at high altitudes.
What causes it? As explained, exposure to high altitudes, though it can also be caused by lung diseases even during sleep apnoea and while diving. It can also occur when inhaling gases such as nitrous oxide or laughing gas.
Haemic hypoxia
What is haemic hypoxia? This type arises from a reduction in the haemoglobin’s capacity to transport oxygen, either through carbon monoxide poisoning, whether from smoking or other causes, or due to severe anaemia and blood loss from haemorrhage or donation.
Ischaemic hypoxia
Results from inadequate perfusion, where blood flow to the tissues is insufficient, especially affecting organs like the brain and heart.
Histotoxic hypoxia
Occurs when cells are unable to utilise oxygen due to intoxication, whether from alcohol, cyanide, or drugs.
Hypoxaemic hypoxia
It is due to a decrease in the oxygen saturation of haemoglobin, despite adequate lung function.